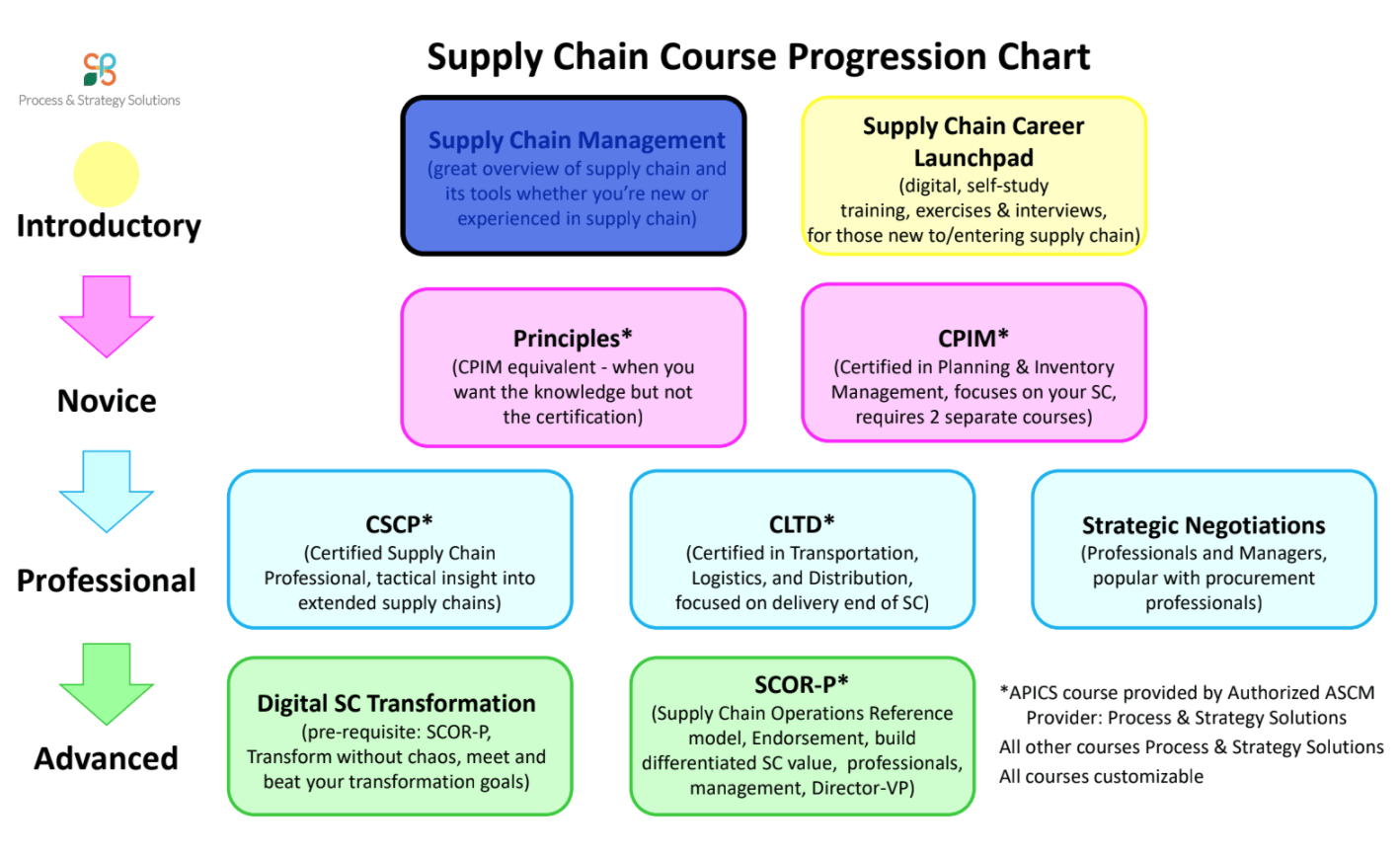
What is Manufacturing? Manufacturing is an added value process that creates goods. It employs labor, machines and chemicals to produce products and services. The manufacturing process is part a secondary sector. It involves both manual and digital labor to create goods. Here are some benefits of manufacturing. Let's look at the manufacturing process and its benefits. This knowledge can be applied to your company.
Manufacturing is a subsector.
Manufacturing, a subsector within the economy, is responsible for creating goods and services. For production to be successful, you need labor, equipment, as well as tools. These processes can include biological or chemical processing. Manufacturing is fundamentally the second sector of the economy. While manufacturing is vital to many other sectors of the economy's economy, it has its own advantages. Here are a few of these benefits.
A strong manufacturing industry is an important component of the U.S. economic engine. While most economists view manufacturing as a purely consumer-oriented industry many others see it as a wealth-generating industry. Manufacturing jobs are crucial to the economy, as they provide middle-class jobs that increase overall wealth. Manufacturing is a job-creating industry that spurs innovation and boosts the economy.
It's a process that adds value.
Activities that modify the form and quality of a product are called value-adding. Cleaning equipment, getting material and lining up equipment are all non-value-added tasks. They also include sorting items for pickup orders, printing paperwork, searching for locations, and searching for them. Automating non value-added activities can make manufacturing more efficient. The following are some examples of activities that can be automated:
Increasing productivity: Manufacturing can be an efficient way of reducing costs and increasing production. In the United States, federal law supports the manufacturing process, which involves physical transformation and large-scale production. Manufacturing has proven to be a successful business model for many industries. Companies are also successful because of their ability to produce large quantities. Manufacturing is an important part of our economy, and should be studied carefully.
It requires manual labour
"Manual Labour" refers to the physical work that humans do. It is distinct to the labour done by machines or working animals. Manual labour consists of doing physical work with one's hands or any other part of the body. It has been the primary method of physical work throughout most of human history. Here are some examples. 1. Agriculture: Most farmers use manual labour, which is often anchored to the crops.
There are several reasons for the correlation between manual and unskilled labour. Intelligence is applicable to nearly any work, including artisanal skills in craft production and logic in applied sciences. However, most workers do not have any formal training. Although education has been a growing necessity in recent centuries, not all workers have the same level of experience. This means that not all jobs require workers who can perform the same tasks in every job.

It makes use of smart technology
Smart manufacturing involves integrating information technology into the manufacturing process, increasing adaptability, using internet-connected machinery, and optimizing performance. It involves collaboration between employees and machines and the use of data analytics to improve production efficiency and profit margins. Smart factories can use interoperable controls and networked sensors to create highly automated systems. They can rapidly respond to changes, increase output and quality, and they can also be highly automated. Smart manufacturing methods don't just apply to one industry.
Artificial intelligence allows smart factories to spot problems before they become major. These advanced technologies can monitor and respond to supply chain changes, reducing downtime costs. Smart factory technology also allows automation of certain processes. This frees engineers up to concentrate on more complex processes. Due to the high upfront cost of smart factories, small businesses may not be financially able invest in them. These technologies are becoming a critical part of manufacturing operations.
FAQ
What is manufacturing and logistics?
Manufacturing is the production of goods using raw materials. Logistics manages all aspects of the supply chain, including procurement, production planning and distribution, inventory control, transportation, customer service, and transport. Sometimes manufacturing and logistics are combined to refer to a wider term that includes both the process of creating products as well as their delivery to customers.
What are the four types of manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process by which raw materials are transformed into useful products through machines and processes. It can involve many activities like designing, manufacturing, testing packaging, shipping, selling and servicing.
How can manufacturing efficiency improved?
The first step is to determine the key factors that impact production time. The next step is to identify the most important factors that affect production time. If you aren't sure where to begin, think about the factors that have the greatest impact on production time. Once you have identified them, it is time to identify solutions.
What is the difference between a production planner and a project manager?
The difference between a product planner and project manager is that a planer is typically the one who organizes and plans the entire project. A production planner, however, is mostly involved in the planning stages.
What are the responsibilities of a logistic manager?
Logistics managers ensure that goods arrive on time and are unharmed. This is accomplished by using the experience and knowledge gained from working with company products. He/she should ensure that sufficient stock is available in order to meet customer demand.
Statistics
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing refers to a method of managing that seeks to improve efficiency and decrease waste. It was developed in Japan during the 1970s and 1980s by Taiichi Ohno, who received the Toyota Production System (TPS) award from TPS founder Kanji Toyoda. Michael L. Watkins published the book "The Machine That Changed the World", which was the first to be published about lean manufacturing.
Lean manufacturing can be described as a set or principles that are used to improve quality, speed and cost of products or services. It emphasizes eliminating waste and defects throughout the value stream. Lean manufacturing is also known as just in time (JIT), zero defect total productive maintenance(TPM), and five-star (S). Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing not only improves product quality but also reduces costs. Companies can also achieve their goals faster by reducing employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is a great way to manage the entire value chain including customers, suppliers, distributors and retailers as well as employees. Lean manufacturing practices are widespread in many industries. Toyota's philosophy has been a key driver of success in many industries, including automobiles and electronics.
Five basic principles of Lean Manufacturing are included in lean manufacturing
-
Define Value- Identify the added value your company brings to society. What makes you stand out from your competitors?
-
Reduce Waste - Remove any activity which doesn't add value to your supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize & Simplify - Make processes as consistent and repeatable as possible.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing has many benefits in the automotive sector. These include higher customer satisfaction, lower inventory levels, lower operating expenses, greater productivity, and improved overall safety.
Any aspect of an enterprise can benefit from Lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing (JIT), also known as "pull system": This form of lean manufacturing is often referred to simply as "pull". JIT stands for a system where components are assembled on the spot rather than being made in advance. This approach reduces lead time, increases availability and reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing: ZDM ensures that no defective units leave the manufacturing plant. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement: Continuous Improvement aims to improve efficiency by continually identifying problems and making adjustments to eliminate or minimize waste. It involves continuous improvement of processes, people, and tools.