
It can be daunting to enter the logistics industry. Before you can get your job, you may need to take additional courses or do internships. There are many entry level jobs in logistics that will help you get started.
These positions usually require an associate's or bachelor's degree. The degree will give you a better understanding of how the supply chain works. A degree will help you become a professional certified. Online classes are also available in specialized subjects. You may be eligible to receive reimbursement for your graduate program.
Many industries offer entry-level jobs in logistics. For instance, you can work in aerospace manufacturing, oil and gas, or in a freight transportation arrangement. There are also opportunities to work internationally, in a variety of industries.
Logistik professionals can use both sides to solve problems. They apply their knowledge to build sustainable supply chains. They can also influence the decision-making process at both the operational and executive levels. While the job can be hard, it can also offer great rewards. The logistics sector is experiencing rapid growth in a boom economy.
Logistics workers must have strong management skills and leadership qualities. They must also communicate effectively. They must also be able to use specialized software systems. They could be responsible for finding storage spaces near shipping ports. They may also be working to ensure that goods are properly cleared at customs.
Logistics is continuously evolving. The logistics industry is continually changing. New technologies and business models are changing how it operates. These changes are important to understand. You will be able to become a competent logistics professional with a bachelor's degree. A bachelor's degree can help you build a professional community. You can also attend seminars and conferences in the industry. A recognized institution may also grant a degree.
There are also a variety of administrative jobs, which require strong communication and analytical skills. Some roles are within the company while others involve customers, suppliers, and other business functions.

You can start your career in logistics by becoming a member a professional association. These organizations offer information about professional certifications, industry news, job board listings, and other useful information. They may also be willing to help you locate a mentor. Some of these organizations also offer graduate fellowships.
There are many countries that offer vocational certifications. These certificates do not require previous logistics experience. These certifications are particularly valuable for companies that have in-house transport fleets. You can also get a Certificate of Professional Competence in Road Transport Operations, which is highly valued by enterprises with in-house transportation fleets.
You can find entry level jobs in logistics all over the country. You can also find a wide range of online resources to help you search for work. You can also rely on the support of your friends and family to get help.
FAQ
What is production management?
Production Planning involves developing a plan for all aspects of the production, including scheduling, budgeting, casting, crew, location, equipment, props, etc. This document aims to ensure that everything is planned and ready when you are ready to shoot. It should also provide information about how best to produce the best results while on set. It should include information about shooting locations, casting lists, crew details, equipment requirements, and shooting schedules.
The first step in filming is to define what you want. You may have already chosen the location you want, or there are locations or sets you prefer. Once you have determined your scenes and locations, it is time to start figuring out the elements that you will need for each scene. If you decide you need a car and don't know what model to choose, this could be an example. This is where you can look up car models online and narrow down your options by choosing from different makes and models.
Once you have found the right car, you can start thinking about extras. What about additional seating? You might also need someone to help you get around the back. Maybe you want to change the interior color from black to white? These questions will help guide you in determining the ideal look and feel for your car. Another thing you can do is think about what type of shots are desired. Do you want to film close-ups, or wider angles? Perhaps you want to show the engine or the steering wheel? These factors will help you determine which car style you want to film.
Once you have made all the necessary decisions, you can start to create a schedule. A schedule will tell you when you need to start shooting and when you need to finish. The schedule will show you when to get there, what time to leave, and when to return home. Everyone knows exactly what they should do and when. You can also make sure to book extra staff in advance if you have to hire them. It is not worth hiring someone who won’t show up because you didn’t tell him.
Also, consider how many days you will be filming your schedule. Some projects can be completed in a matter of days or weeks. Others may take several days. You should consider whether you will need more than one shot per week when creating your schedule. Multiplying takes in the same area will result both in increased costs and a longer time. It's better to be safe than sorry and shoot less takes if you're not certain whether you need more takes.
Budgeting is another important aspect of production planning. It is important to set a realistic budget so you can work within your budget. You can always lower the budget if you encounter unexpected problems. It is important to not overestimate how much you will spend. You'll end up with less money after paying for other things if the cost is underestimated.
Production planning is a detailed process. But, once you understand the workings of everything, it becomes easier for future projects to be planned.
What jobs are available in logistics?
There are many jobs available in logistics. Here are some examples:
-
Warehouse workers - They load trucks and pallets.
-
Transportation drivers: They drive trucks and trailers and deliver goods and make pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers - They sort and pack freight in warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents - They purchase goods and services needed for company operations.
-
Customer service representatives - They answer calls and emails from customers.
-
Shippers clerks - They process shipping order and issue bills.
-
Order fillers - These people fill orders based on what has been ordered.
-
Quality control inspectors (QCI) - They inspect all incoming and departing products for potential defects.
-
Others - There is a variety of other jobs in logistics. These include transportation supervisors and cargo specialists.
Is automation important for manufacturing?
Not only is automation important for manufacturers, but it's also vital for service providers. They can provide services more quickly and efficiently thanks to automation. They can also reduce their costs by reducing human error and improving productivity.
How can overproduction in manufacturing be reduced?
The key to reducing overproduction lies in developing better ways to manage inventory. This would reduce the time spent on unproductive activities like purchasing, storing and maintaining excess stock. We could use these resources to do other productive tasks.
You can do this by adopting a Kanban method. A Kanban board is a visual display used to track work in progress. A Kanban system allows work items to move through several states before reaching their final destination. Each state has a different priority level.
As an example, if work is progressing from one stage of the process to another, then the current task is complete and can be transferred to the next. However, if a task is still at the beginning stages, it will remain so until it reaches the end of the process.
This allows for work to continue moving forward, while also ensuring that there is no work left behind. With a Kanban board, managers can see exactly how much work is being done at any given moment. This information allows them to adjust their workflow based on real-time data.
Lean manufacturing can also be used to reduce inventory levels. Lean manufacturing works to eliminate waste throughout every stage of the production chain. Anything that doesn't add value to the product is considered waste. Here are some examples of common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Overstock materials
Manufacturers can reduce their costs and improve their efficiency by using these ideas.
What is the difference in Production Planning and Scheduling, you ask?
Production Planning (PP), or production planning, is the process by which you determine what products are needed at any given time. Forecasting and identifying production capacity are two key elements to this process.
Scheduling refers to the process of allocating specific dates to tasks in order that they can be completed within a specified timeframe.
What does "warehouse" mean?
A warehouse, or storage facility, is where goods are stored prior to being sold. It can be either an indoor or outdoor space. Sometimes, it can be both an indoor and outdoor space.
Statistics
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use lean manufacturing in the Production of Goods
Lean manufacturing is an approach to management that aims for efficiency and waste reduction. It was developed by Taiichi Okono in Japan, during the 1970s & 1980s. TPS founder Kanji Takoda awarded him the Toyota Production System Award (TPS). The first book published on lean manufacturing was titled "The Machine That Changed the World" written by Michael L. Watkins and published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing, often described as a set and practice of principles, is aimed at improving the quality, speed, cost, and efficiency of products, services, and other activities. It emphasizes the elimination of defects and waste throughout the value stream. Just-in-time (JIT), zero defect (TPM), and 5S are all examples of lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing seeks to eliminate non-value added activities, such as inspection, work, waiting, and rework.
Lean manufacturing improves product quality and costs. It also helps companies reach their goals quicker and decreases employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is considered one of the most effective ways to manage the entire value chain, including suppliers, customers, distributors, retailers, and employees. Many industries worldwide use lean manufacturing. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Lean manufacturing includes five basic principles:
-
Define Value - Determine the value that your business brings to society. Also, identify what sets you apart from your competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Eliminate any activity that doesn't add value along the supply chain.
-
Create Flow: Ensure that the work process flows without interruptions.
-
Standardize and Simplify – Make processes as consistent, repeatable, and as simple as possible.
-
Build Relationships - Establish personal relationships with both internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing, although not new, has seen renewed interest in the economic sector since 2008. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. According to some economists, lean manufacturing could be a significant factor in the economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is now becoming a common practice in the automotive industry, with many benefits. These include better customer satisfaction and lower inventory levels. They also result in lower operating costs.
The principles of lean manufacturing can be applied in almost any area of an organization. It is especially useful for the production aspect of an organization, as it ensures that every step in the value chain is efficient and effective.
There are three main types in lean manufacturing
-
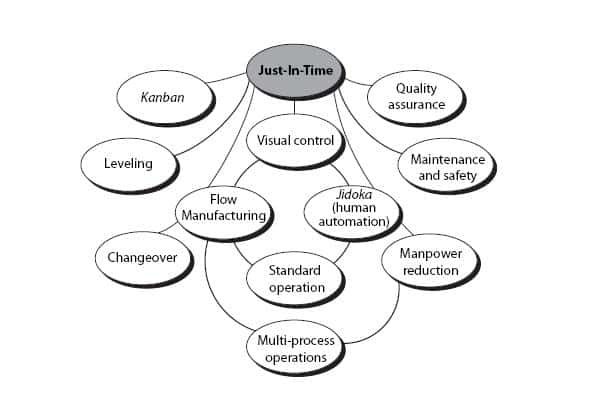
Just-in Time Manufacturing (JIT), also known as "pull system": This form of lean manufacturing is often referred to simply as "pull". JIT refers to a system in which components are assembled at the point of use instead of being produced ahead of time. This strategy aims to decrease lead times, increase availability of parts and reduce inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM): ZDM focuses on ensuring that no defective units leave the manufacturing facility. Repairing a part that is damaged during assembly should be done, not scrapping. This applies to finished goods that may require minor repairs before shipment.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI),: Continuous improvement aims improve the efficiency and effectiveness of operations by continuously identifying issues and making changes to reduce waste. It involves continuous improvement of processes, people, and tools.