The best lean books provide invaluable guidance for industry leaders by using simple language and clear explanations. The bestseller covers a variety of concepts such as how to improve business processes, reduce costs and improve quality. Detailed drawings and step-by-step instructions make implementation easy. You will also find information about various tools for lean manufacturing in the book.
It also gives an overview of Toyota's production system and its global success. It also describes Toyota's motivation, problem solving and management style. It provides details about Toyota's Lean strategy's success and explains 14 management principles that are the basis of Toyota's business operations. The book also has a chapter on Toyota's automotive industry. It includes a section that explains how Toyota uses lean principles in the sector.
Lean manufacturing, or lean manufacturing, is a manufacturing method that aims at improving the quality of the products and/or services that a company produces. It aims to eliminate waste, making the process more efficient and error-free. High-skilled people and machines are key to successful manufacturing processes. These interactions make up the majority of manufacturing company costs.
The best books on lean manufacturing include the Lean Manufacturing Tool Book, The Toyota Way: 14 Management Principles for Improving Quality and Productivity, and The Machine that Changed the World: How Toyota Built a Competitive Advantage. These books give a detailed explanation of Toyota's production system, as well as practical tips and instructions on how to apply Lean techniques in any manufacturing environment. Lean Manufacturing Tool Book is a comprehensive guide to the tools and techniques used in Lean manufacturing. The book provides expert advice to help you choose the right tool and lists the available tools. It also discusses Lean manufacturing concepts such as Six Sigma and Lean problem solving.
The Toyota Way is one of the first books to introduce Lean manufacturing. It is a guide to Toyota's management principles. You will also learn how to implement these principles within your own company. It includes information on the organization profiles as well as the philosophies that underpin Toyota's success. A new afterword discusses Lean's impact on the manufacturing sector since the book was published. It provides new frameworks to improve quality and reduce costs, as well as updated production processes.
The Machine that Changed the World - How Lean Changed the World - This book was the first to fully explain the Toyota Production System, and the impact it had on the manufacturing industry. This book was published in 1990. It provides an overview and context of the system. It contains a revised afterword and foreword which provide a deeper understanding of Toyota Production System and its effect on global manufacturing. It also explains what the fundamental ideas are that underpin Lean today.

Another important book is The Toyota Kata: Flow Focused Manufacturing Methodology. It describes how Toyota works closely with customers to deliver quality products and services. It explains Toyota's commitment towards quality, problem-solving, speeding up business operations and ensuring customer satisfaction. It also explains Toyota's selection and hiring process and the motivation of employees to provide high quality products.
FAQ
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The acronym "7R's" of Logistics stands for seven principles that underpin logistics management. It was developed by the International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL) and published in 2004 as part of its "Seven Principles of Logistics Management" series.
The acronym is made up of the following letters:
-
Responsible – ensure that all actions are legal and don't cause harm to anyone else.
-
Reliable: Have faith in your ability or the ability to honor any promises made.
-
Reasonable - use resources efficiently and don't waste them.
-
Realistic – Consider all aspects, including cost-effectiveness as well as environmental impact.
-
Respectful - treat people fairly and equitably.
-
You are resourceful and look for ways to save money while increasing productivity.
-
Recognizable - provide customers with value-added services.
Is it necessary to be familiar with Manufacturing Processes before we learn about Logistics.
No. No. However, knowing about manufacturing processes will definitely give you a better understanding of how logistics works.
What is the job of a production plan?
Production planners make sure that every aspect of the project is delivered on-time, within budget, and within schedule. They ensure that the product or service is of high quality and meets client requirements.
What are the four types in manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials into useful products using machines and processes. Manufacturing involves many activities, including designing, building, testing and packaging, shipping, selling, service, and so on.
What makes a production planner different from a project manger?
The primary difference between a producer planner and a manager of a project is that the manager usually plans and organizes the whole project, while a production planner is only involved in the planning stage.
How can we increase manufacturing efficiency?
First, we need to identify which factors are most critical in affecting production times. We then need to figure out how to improve these variables. If you don’t know where to begin, consider which factors have the largest impact on production times. Once you've identified them, try to find solutions for each of those factors.
What does it mean to warehouse?
A warehouse or storage facility is where goods are stored before they are sold. It can be an outdoor or indoor area. In some cases, it may be a combination of both.
Statistics
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
External Links
How To
How to use lean manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing is a management style that aims to increase efficiency and reduce waste through continuous improvement. It was first developed in Japan in the 1970s/80s by Taiichi Ahno, who was awarded the Toyota Production System (TPS), award from KanjiToyoda, the founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
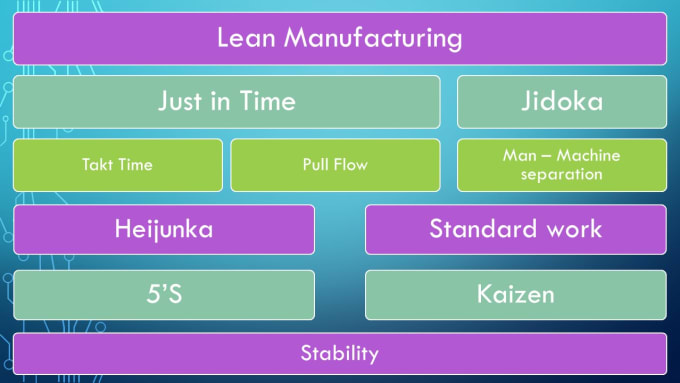
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes the elimination of defects and waste throughout the value stream. Lean manufacturing is called just-in-time (JIT), zero defect, total productive maintenance (TPM), or 5S. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean manufacturing is considered one of the most effective ways to manage the entire value chain, including suppliers, customers, distributors, retailers, and employees. Lean manufacturing practices are widespread in many industries. Toyota's philosophy has been a key driver of success in many industries, including automobiles and electronics.
Lean manufacturing includes five basic principles:
-
Define Value: Identify the social value of your business and what sets you apart.
-
Reduce waste - Get rid of any activity that does not add value to the supply chain.
-
Create Flow – Ensure that work flows smoothly throughout the process.
-
Standardize and Simplify – Make processes as consistent, repeatable, and as simple as possible.
-
Build Relationships- Develop personal relationships with both internal as well as external stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing has always been around, it is gaining popularity in recent years because of a renewed interest for the economy after 2008's global financial crisis. Many businesses have adopted lean production techniques to make them more competitive. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is becoming a popular practice in automotive. It has many advantages. These include higher customer satisfaction, lower inventory levels, lower operating expenses, greater productivity, and improved overall safety.
You can apply Lean Manufacturing to virtually any aspect of your organization. Lean manufacturing is most useful in the production sector of an organisation because it ensures that each step in the value-chain is efficient and productive.
There are three main types in lean manufacturing
-
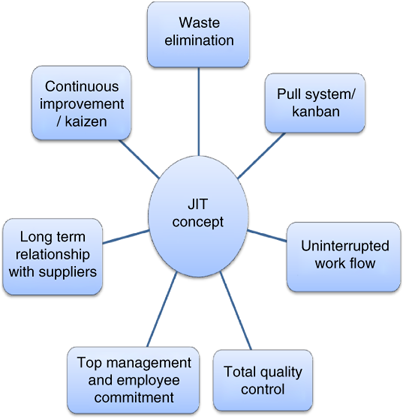
Just-in Time Manufacturing: This lean manufacturing method is commonly called "pull systems." JIT means that components are assembled at the time of use and not manufactured in advance. This method reduces lead times, increases availability, and decreases inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM),: ZDM is a system that ensures no defective units are left the manufacturing facility. If a part needs to be fixed during the assembly line, it should be repaired rather than scrapped. This also applies to finished products that need minor repairs before being shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI), also known as Continuous Improvement, aims at improving the efficiency of operations through continuous identification and improvement to minimize or eliminate waste. Continuous improvement involves continuous improvement of processes and people as well as tools.